Practice for Movement
Spinal Galant Reflex
The movement:
When the lower back is touched next to the spine and / or under the influence of sound vibrations in the balance organ, the hip on the touched side turns up 45° in the direction of the touch. This reflex transmits sound vibrations to the organism and plays a role in transferring stimuli between the head and pelvis. The connection goes through the backbone. This reflex increases mobility and makes you restless.
Symptoms of an uninhibited Spinal Galant Reflex:
- No stable center of gravity in your pelvis
- Poor balance
- Three-dimensional movements of the pelvis are impeded
- Rigid pelvis that simultaneously exhibits a weak and cramped muscle tone. When the lower back is stiffened and / or weakened, the shoulder area and the middle back are also obstructed
- Can only become toilet trained very late or not at all, because the urinary reflex is triggered by the Spinal Galant Reflex
- Hardening of connective tissue and cartilage
- Reduced blood flow in the pelvic area
- Overall posture deteriorates, entrapment or subsidence of organs
- A range of back and shoulder malaise can arise; pain, 'worn out' cartilage, crookedness, scoliosis, cramping, pinching nerves, problems with pregnancies, giving birth to a child and after giving birth pelvic instability.
- Being unable to sit still: wriggling, bouncing, fiddling, twisting, nerve tics in the face, tapping or drumming with hands and / or feet
- Irritable due to tight clothes
- Fluttering attention
- Concentration problems
- Unrest
- Hypersensitive to vibrations in the balance organ or to noise
- Worrying, grinding and therefore falling asleep badly
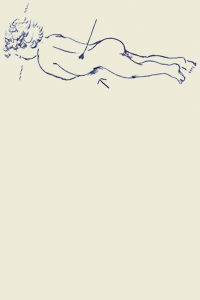
exercises:
pdf: exercises